Retinal Detachment Treatment
Retinal detachment is the separation of the retinal layer inside the eye from the epithelium due to the membranes or the fluid accumulating under it.
The retina is a very light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye, allowing images to be perceived. Retinal detachment can interfere with the normal function of the retinal layer and cause severe vision loss. There are 3 different varieties of it. These are: rhegmatogenous, that is, torn; tractional, that is, retracted, and exudative.
The retinal tear is the tearing of the retinal layer. This problem is one of the most common causes of retinal detachment. It can be seen in people of almost all ages, depending on both hereditary and environmental factors. It can also cause the fluid in the eye to leak under the retinal layer. Retinal tears may also cause symptoms such as dark spots in the eye, illusions of light, and blurred vision.
Retinal detachment or tear is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. If left untreated, it can cause blindness. When the symptoms of this problem are noticed, the person should consult an ophthalmologist without wasting time.
What are the Symptoms of Retinal Tear?
Retinal tear symptoms can vary from person to person. However, the following symptoms are signs that suggest the presence of this condition:
- A sudden and severe illusion or flash of light in the eye
- Dark spots in the eye, curtain, or foggy vision
- Presence of moving or fixed points that suddenly appear in the field of view
- Decreased visual acuity or blurred vision
- Visualizing, flashing, or streaking in the same eye multiple times
Approximately 30% of patients with these symptoms are diagnosed with retinal tear. If these symptoms persist, 50% of the people in the same group have a retinal detachment. It's a problem that can usually be detected in advanced stages since there is no symptom in the beginning.
How is Retinal Detachment Treatment?
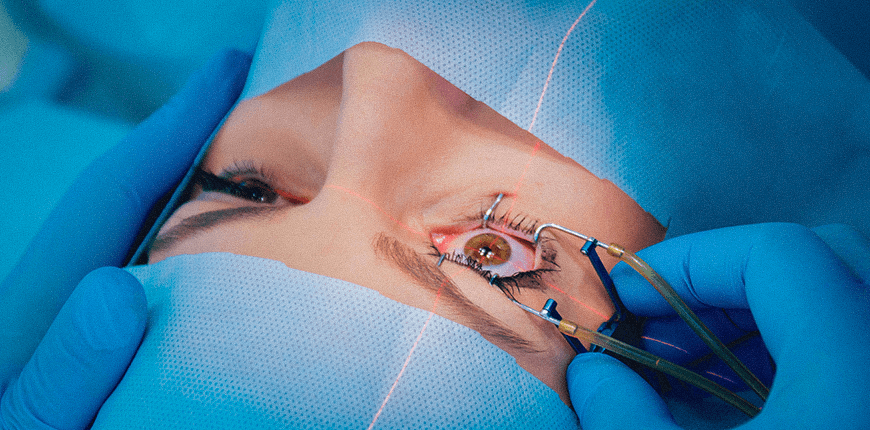
 Retinal detachment is the separation of the retinal layer from its normal position inside the eye. This can lead to progressive visual loss and even lead permanent blindness. Treatment may vary depending on the cause, type, and severity of the problem. The most commonly preferred methods are listed.
Retinal detachment is the separation of the retinal layer from its normal position inside the eye. This can lead to progressive visual loss and even lead permanent blindness. Treatment may vary depending on the cause, type, and severity of the problem. The most commonly preferred methods are listed.
-
Laser Therapy: This method is mostly used in the treatment of small-scale retinal detachment. By applying it to a correctable part of the retinal layer, the retinal layer is reattached. The experience of the physician is very important.
- Pneumatic Retinopexy: It is another method used in the treatment of retinal detachment. In this method, gas is injected into the eye and the retinal layer is reattached. The gas bubble is placed in the lower part of the eye and keeps the patient's head in a certain position, sticking the retinal layer in place.
- "Scleral buckle" Surgery: Scleral buckle surgery is one of the most commonly used methods in the treatment of retinal detachment. In this method, an average of 5 mm silicone or rubber band is placed on the white part of the eye, thereby increasing the pressure inside the eye and sticking the retina layer in its place.
- Vitrectomy: This surgery is a preferred surgical method in more severe cases. In this method, the vitreous fluid, which is the gel-like inner part of the eye, is removed by the surgeon and reinserted. During this procedure, the conjunctiva is opened and 3 incisions are made from here. If there are excess membranes and tissues accumulated in the area, they are cleaned. Then, special substances are placed in the same area as a buffer. It is an application that takes about 1.5 hours.
Treatment of retinal detachment is carried out using one of these methods, depending on the patient's condition. Which method will be used is determined by the doctor after the examinations.
Vision After Retinal Detachment Surgery
After retinal detachment surgery, the quality of vision of the person may vary depending on many factors. The severity of the retinal tear before the operation, the location of the tear, the procedures performed during the operation, the occurrence of complications, the care in the postoperative period, and the general health of the patient are among the factors that directly affect the outcome of the operation.
However, retinal detachment surgeries are mostly successful, and most patients recover completely. After the operation, the patients need to keep their eyes in certain positions for a certain period of time for a few days to a week. In addition, it's very important to use the drugs prescribed by the doctor and not delay the postoperative controls.
While most of the patients report that their visual disturbances are resolved after surgery, they largely return to their pre-operative level of vision.
Following the doctor's recommendations and performing regular care in the pre-op and post-op processes ensure that patients have a smooth recovery process and regain their vision.
-
When does Retinal Detachment heal?
The healing process after retinal detachment surgery may vary from person to person. Usually, it takes up to 6-8 weeks to see a full recovery.
-
Is Retinal Detachment surgery risky?
Retinal detachment surgery, like other surgical operations, carries some risks. However, this may vary depending on the patient's condition, the extent of the surgery, and the techniques used. In the consultation before the surgery, the patient is informed in detail.
-
What should I pay attention to after Retinal Detachment surgery?
After retinal detachment surgery, it's very important to follow your doctor's recommendations. These ones may include the use of medication, eyewash, and other special care. During the post-op period, you may need to avoid heavy activities, and wear an eye bandage to protect your eye.